What is VMware Data Recovery? A Complete Guide to Virtual Machine Data Protection
In today's digital landscape, where businesses rely heavily on virtualized environments, data loss can be catastrophic. For companies using VMware, the question "What is VMware Data Recovery" is fundamental to ensuring business continuity. It refers to the suite of tools, methodologies, and practices designed to back up and restore data within a VMware virtual environment. This process is crucial for protecting against data loss from accidental deletion, hardware failure, cyber-attacks, or corruption. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of VMware Data Recovery, explaining its core concepts, how it works, and the best practices for implementation, giving you the knowledge to effectively safeguard your virtual infrastructure.
Understanding the Virtual Environment: VMDK and VMFS
To fully grasp what is VMware Data Recovery, one must first understand the key components of a VMware virtual environment.
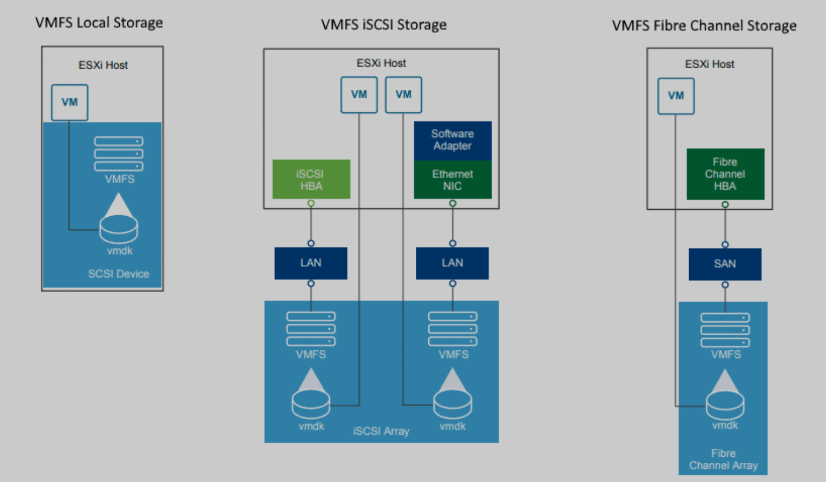
VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk) Files: A VMDK file is a container that encapsulates an entire virtual machine (VM), including its operating system, applications, and all associated data. It functions like a physical hard drive for the VM, stored as a single file (with a
.vmdkextension) on a physical storage device. When you perform data recovery, you are often recovering or restoring these VMDK files or the data within them.VMFS (Virtual Machine File System): This is the high-performance cluster file system that VMware uses to store VMDK files on physical storage like SAN, NAS, or local disks. VMFS allows multiple ESXi hosts to access the same storage pool simultaneously, enabling essential features like vMotion and Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS). Recovery may sometimes be needed at the entire VMFS level if the file system itself becomes corrupted.
How Does VMware Data Recovery Work?
VMware Data Recovery operates through several mechanisms, ranging from built-in features to specialized third-party tools. The core principle involves creating a copy of the virtual machine's state and data, which can be used to restore the VM to a previous point in time.

1. Native VMware Snapshots
A snapshot captures the entire state of a virtual machine at a specific moment, preserving its disk, memory, and power settings.
Creation and Function: When you create a snapshot, the system generates a delta VMDK file. All subsequent writes made by the VM are directed to this new file, leaving the original base VMDK untouched. This allows you to preserve the VM's state before a significant change, like a software update.
Recovery Process: If an issue arises, you can quickly revert the VM to the state it was in when the snapshot was taken. This is fast and effective for short-term recovery needs.
Limitations and Risks: Snapshots are not a long-term backup solution. They can consume significant storage space as they grow, and having multiple snapshots can severely impact VM performance due to the I/O overhead of traversing the snapshot chain. If a VMFS volume fills up due to unchecked snapshot growth, it can lead to VM crashes.
2. Dedicated Backup and Recovery Tools
For robust, long-term data protection, dedicated tools are necessary. These solutions leverage VMware's vStorage APIs for Data Protection (VADP) to perform backups efficiently.
Image-Level Backups: Modern tools typically perform image-level backups, which means they back up the entire VM as a single entity (the VMDK file) rather than the individual files inside it. This is more efficient than traditional file-based backups.
Deduplication: To optimize storage, these solutions often include deduplication. This technology eliminates redundant data blocks across multiple VMs or backups, drastically reducing the required storage capacity.
Permanent Incremental Backups: Instead of taking full backups every time, solutions use a "permanent incremental" model. An initial full backup is created, and all subsequent backups only capture the data that has changed since the last backup. Each incremental backup is synthetically linked to create a full recovery point, meaning any backup can be used for a direct restore without a lengthy consolidation process.
Application-Consistent Backups: To ensure that applications like databases recover correctly, tools use mechanisms like Microsoft's Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) inside Windows-based VMs. This coordinates with the OS and application to flush buffers and create a backup that is logically consistent, as if the application was shut down gracefully.
3. Advanced Recovery Scenarios and Tools
In cases of severe corruption or loss where standard backups are unavailable, specialized data recovery software may be required.
VMDK File Repair: Tools like SysTools VMware Recovery can scan, recover, and extract data from corrupted, deleted, or formatted VMDK files directly, without needing an active ESXi environment.
VMFS Recovery: In events where an entire VMFS volume is damaged or lost—for example, due to a RAID failure—specialized systems like the VMFS Recover System can be used to reconstruct the file system and extract VMDK files from the raw storage.
Key Features of an Effective VMware Data Recovery Solution
When evaluating solutions, you should look for several key features that define a modern and capable recovery system:

Centralized Management: The ability to manage backups for an entire data center from a single pane of glass.
Flexible Recovery Granularity: Support for restoring an entire VM, individual files from within a VM (File-Level Restore), or even specific application items.
Storage and Cloud Agnosticism: The solution should work with a variety of storage backends, including SAN, NAS, and CIFS-based storage like SAMBA.
Integration with vCenter: Tight integration allows for centralized scheduling and the ability to back up VMs even if they have been moved by vMotion or DRS.
Encryption and Security: All backup data should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
Backup Verification: Features that automatically verify the integrity of backup files to ensure they are not corrupted and are usable for a restore.
Why is a VMware Data Recovery Strategy So Critical?
The consequences of data loss in a virtual environment can be severe.
Minimize Costly Downtime: According to industry data, downtime can cost businesses an average of over $1,400 per minute. A swift recovery process directly mitigates these financial losses.
Compliance and Legal Protection: Many industries are governed by regulations (like GDPR or HIPAA) that mandate data protection and recovery capabilities. A robust strategy helps avoid heavy fines and legal penalties.
Protect Against Evolving Threats: With the rise of ransomware and other cyber-attacks, having isolated, recoverable backups is the last line of defense to restore operations without paying a ransom.
Address the Full Spectrum of Data Loss: Data can be lost for many reasons, including accidental deletion, logical corruption, hardware failure (like a "Purple Screen of Death" on an ESXi host), and natural disasters. A comprehensive recovery plan addresses all these scenarios.
Best Practices for Implementing VMware Data Recovery
Simply having a tool is not enough. Adhering to best practices is key to a successful data protection strategy.
Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Maintain at least 3 copies of your data, on 2 different types of media, with 1 copy stored off-site or in the cloud. Many solutions support remote replication to facilitate this.
Schedule Regular Backups and Test Restores: Automate your backup schedules to ensure consistency. Crucially, periodically perform test restores to validate that your backups are working correctly and that you can meet your Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) .
Use Snapshots Wisely: Reserve snapshots for short-term operational needs, such as applying patches, and remove them immediately after the task is complete to avoid performance degradation and storage issues.
Monitor and Manage Storage Capacity: Keep a close eye on the storage capacity for your backups and VMFS datastores. Proactively manage space to prevent failures caused by running out of room.
Leverage Application-Consistent Backups: For any VM running transactional applications like databases or email servers, always ensure your backup method is application-consistent to prevent data corruption upon restore.
Conclusion
Understanding what is VMware Data Recovery is the first step toward building a resilient virtual infrastructure. It is a multi-faceted discipline that combines native VMware technologies like snapshots with powerful, dedicated backup solutions to protect against data loss. By implementing a well-architected recovery strategy that includes the right tools, rigorous processes, and adherence to proven best practices like the 3-2-1 rule, organizations can confidently ensure business continuity, maintain compliance, and securely navigate the challenges of the modern digital world.